

 |
 |
Abstract
Simple Wing Design Optimized for Mass and Drag
Purpose – To optimize the parameters of the wing of a jet transport aircraft with equations from the aircraft design on wing mass and drag in a spreadsheet (Excel) and with its optimizer (Solver). ---
Methodology – The wing mass is calculated using Torenbeek's equation (with and without wing strut) and alternatively using an equation from the Luftfahrttechnischen Handbuch (LTH). Drag is divided into zero-lift drag, induced drag, and wave drag. The respective methods for calculating these drag elements are taken from Scholz's lecture notes. The aircraft design is mapped in a simplified way without the many hierarchically structured iterations. Instead, this simple wing design uses only one iteration. Procedures with snowball effect (Mass Growth Factor), with the 1st law of aircraft design and with both procedures combined are examined. On the one hand, the drag (fuel consumption) is minimized and, on the other hand, the take-off mass, which can be seen as a proxy for Direct Operating Costs (DOC). ---
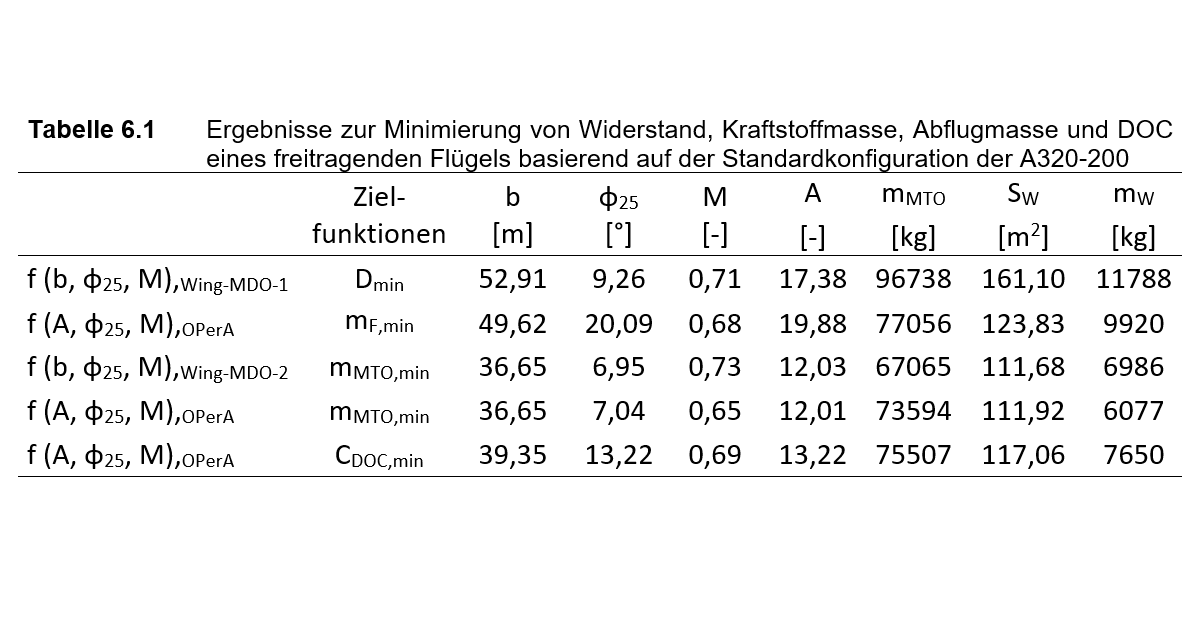
Findings – The simple approach to Multidisciplinary Design Optimization (MDO) is provided as a spreadsheet "Wing-MDO". In comparison with the complete aircraft design and optimization program "Optimization in Preliminary Aircraft Design" (OPerA), the results from the simpler "Wing-MDO" could be confirmed or calibrated to it. A further comparison resulted from the literature review. For an aircraft with parameters like the Airbus A320, an optimal wingspan is obtained by minimizing the drag of 42.52 m (-23.94 %) without a wing brace and 53.09 m (-24.50 %) using a wing brace and minimizing the take-off mass an optimal wingspan of 36.65 m (-8.76 %) or 44.20 m (-13.31 %). The resulting changes in drag or take-off mass are given in parentheses. ---
Practical Implications – "Wing-MDO" is offered to the community as a simple and user-friendly tool in Excel for optimizing basic wing parameters. ---
Social Implications – The optimization of an aircraft traditionally starts with the wing. This can currently also be seen in the new Boeing X-66A project. The present thesis serves to classify such proposals and shows that wings with a high span (and aspect ratio) can significantly reduce fuel consumption and thus CO2 emissions and environmental impact. Presented simple calculations make public discourse possible. ---
Originality – Disciplines have presented the impact of their investigations at aircraft level, without considering the iterations (snowball effects) of aircraft design. Using the example of the wing, it could be shown how individual effects on mass and drag can be transferred simply but correctly to the aircraft level.
| Download full text: |
 TextMahfouzMaster.pdf
Size:
2.2M TextMahfouzMaster.pdf
Size:
2.2M |
| Date: | 2023-10-16 |
| Type of work: | Master Thesis |
| Advisor / Examiner: | Dieter Scholz |
| Published by: | Aircraft Design and Systems Group (AERO), Department of Automotive and Aeronautical Engineering, Hamburg University of Applied Sciences |
This work is part of: |
Digital Library - Projects & Theses - Prof. Dr. Scholz ---
http://library.ProfScholz.de
 |
| Download presentation: |
 VortragMahfouzMaster.pdf
Size:
1.2M VortragMahfouzMaster.pdf
Size:
1.2M
|
| Download poster: |
 AERO_POS_DLRK2024_Fluegelentwurf_2024-09-30
Size:
534K AERO_POS_DLRK2024_Fluegelentwurf_2024-09-30
Size:
534K
|
| Persistent identifier: | https://doi.org/10.48441/4427.2124 |
| PERSISTENT IDENTIFIER: | |
| URN: | https://nbn-resolving.org/urn:nbn:de:gbv:18302-aero2023-10-16.018 (to reach this page) |
| DOI: | https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15620524 |
| ARK: | https://n2t.net/ark:/13960/s2f41vh0358 |
| Associated research data: | https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/9OVFDO (Program) |
| URLs registered with URN: | Show all links associated with this text! |
| CATALOG ENTRY: | |
| DNB: | Check inclusion of this title in German National Library! |
| WorldCat: | Check inclusion of this title in WorldCat! |
| DataCite: | Check inclusion of this title in DataCite! |
| Google Scholar: | Check inclusion of this title in Google Scholar! |
| OpenAIRE: | Check inclusion of this title in OpenAIRE! |
| Semantic Scholar: | Check inclusion of this title in Semantic Scholar! |
| BASE: | Check inclusion of this title in BASE! |
| CORE: | Check inclusion of this title in CORE! |
| Google: | Check inclusion of this title in Google! |
| Keywords, German (GND): | Luftfahrt, Verkehrsflugzeug, Flügel, Optimierung |
| Keywords, English (LCSH): | Aeronautics, Airplanes, Design, Airplanes--Wings |
| Keywords, free: | aerospace engineering, spreadsheet aerodynamics, structures, economics, Boeing, X-66A, MDO, DOC, aircraft, mass, operating empty mass, mass, drag, Luftfahrzeug, Flugzeugbau, Flugzeug, Flugzeugentwurf, Masse, Aerodynamic, Struktur, Betriebsleermasse |
| DDC: | 629.13, 629.1341, 629.1323, 629.13432 |
| RVK: | ZO 7205 |
© This work is protected by copyright
The work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License
CC BY-NC-SA
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0

Any further request may be directed to:
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Dieter Scholz, MSME
E-Mail see: http://www.ProfScholz.de
VISIBILITY: (more)
Quote this text:
| ISO 690: MAHFOUZ, Houssein, 2023. Einfacher Flügelentwurf optimiert hinsichtlich Masse und Widerstand. Master Thesis. Hamburg University of Applied Sciences, Aircraft Design and Systems Group (AERO). Available from: https://nbn-resolving.org/urn:nbn:de:gbv:18302-aero2023-10-16.018 [viewed YYYY-MM-DD]. |
Major results / graphical abstract:
 Prof. Dr. Scholz
Prof. Dr. Scholz
 Aircraft Design and Systems Group (AERO)
Aircraft Design and Systems Group (AERO)
 Aeronautical Engineering
Aeronautical Engineering
 Department of Automotive and Aeronautical Engineering
Department of Automotive and Aeronautical Engineering
 Faculty of Engineering and Computer Science
Faculty of Engineering and Computer Science
 Hamburg University of Applied Sciences
Hamburg University of Applied Sciences