The ratio 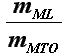 "maximum landing mass to maximum takeoff mass"
"maximum landing mass to maximum takeoff mass"
is needed to calculate the landing field- and the missed approach condition
because in the matching chart all values refer to the maximum take off mass.
In preliminary sizing according to LOFTIN 1980 the mass ratio is chosen from statistics.
Loftin determined a statistic with mean values for three range categories:
| Range class | Range in [ N.M. ] | Range in [ km ] | mML / mMTO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Short Range | 1000 - 1500 | 1800 - 2800 | 0.91 |
| Middle Range | 2000 - 3000 | 3700 - 5600 | 0.82 |
| Long Range | 3000 - 4000 | 5600 - 7400 | 0.73 |
| Airplane Type | mML / mMTO | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Average | Maximum | ||
| 1. Homebuilts | 0.96 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |
| 2. Single Engine Propeller Driven | 0.95 | 0.997 | 1.0 | |
| 3. Twin Engine Propeller Driven | 0.88 | 0.99 | 1.0 | |
| 4. Agricultural | 0.7 | 0.94 | 1.0 | |
| 5. Business Jets | 0.69 | 0.88 | 0.96 | |
| 6. Regional TBP | 0.92 | 0.98 | 1.0 | |
| 7. Transport Jets | 0.65 | 0.84 | 1.0 | |
| 8. Military Trainers | 0.87 | 0.099 | 1.1 | |
| 9. Fighters | (Jets) | 0.78 | N/A | 1.0 |
| (TBP's) | 0.57 | N/A | 1.0 | |
| 10. Mil. Patrol, Bomb and Transport | (Jets) | 0.68 | 0.76 | 0.83 |
| (TBP's) | 0.77 | 0.084 | 1.0 | |
| 11. Flying Boats, Amphibious and Float Airplanes | (land) | 0.79 | N/A | 0.95 |
| (water) | 0.98 | N/A | 1.0 | |
| 12. Supersonic Cruise Airplanes | 0.63 | 0.75 | 0.88 | |
|
|